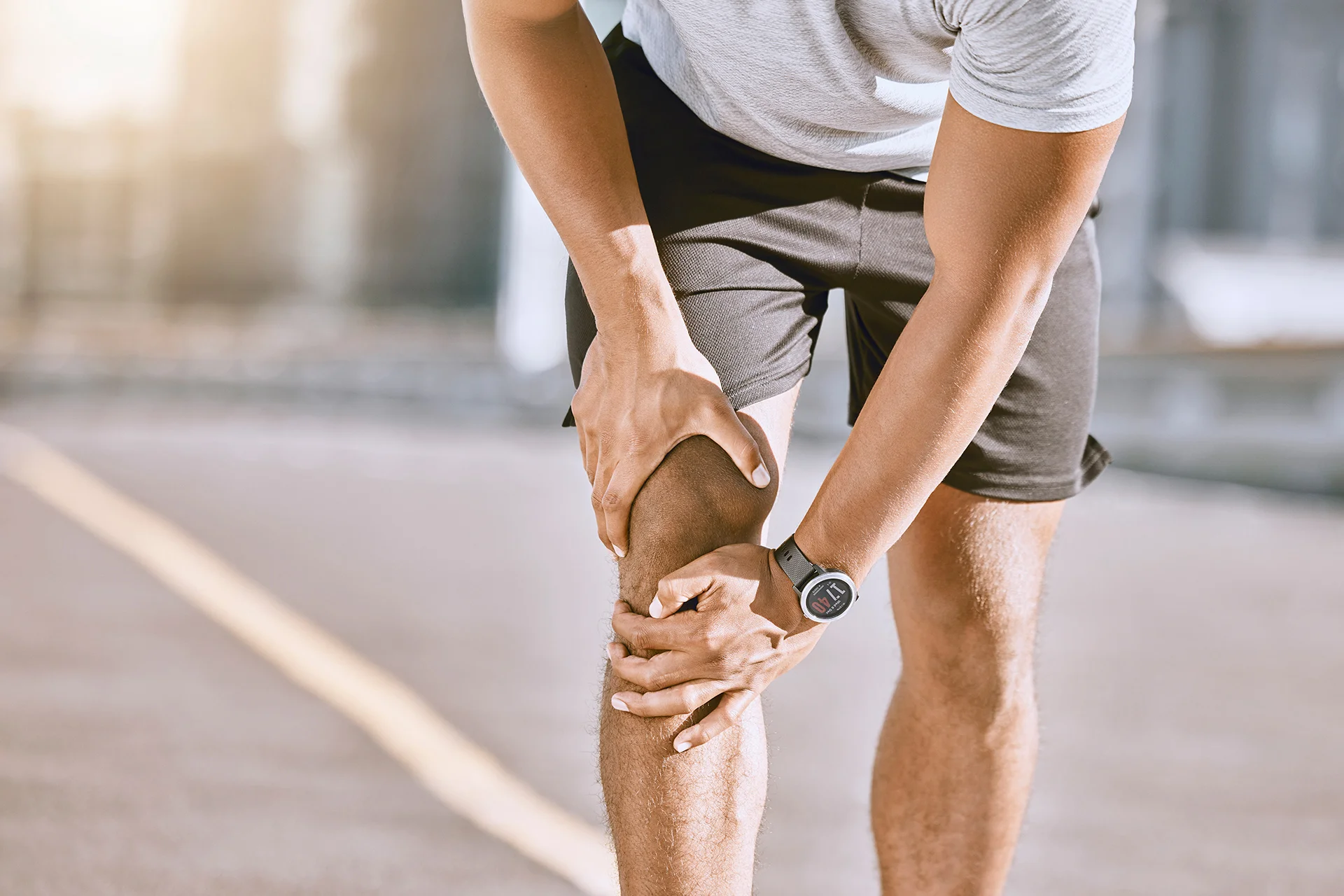
Joint pain can become an unpleasant daily challenge that affects your overall quality of life. Although it is often a natural part of the ageing process, sometimes joint pain occurs much earlier due to chronic diseases, injuries or even genetics. This time, together with Drops Clinic’s family doctors, we’ll delve into the causes of joint pain and discuss possible treatment methods.
Types of joint pain
Joint pain is a widespread problem that can affect joints in the knees, shoulders, elbows or even hands. These pains are often caused by a variety of reasons that affect the function and structure of the joints.
There are several types of joint pain, depending on how and where in the body the pain occurs:
Knee joint pain
This is one of the most common types of joint pain. The knees bend more than a million times a year and bear intense pressure and strain every day. It is therefore not surprising that knee pain occurs in people of all ages.
Knee pain can be caused by trauma or inflammation of the joint. Often, it can be caused by overloading of the joint, for example from intense sports or prolonged sitting. However, knee pain is most often associated with ligament injuries.
It is not uncommon to have pain specific to this joint. These include baker’s cyst, runner’s knee and meniscal tears.
Pain may be accompanied by discomfort, swelling and limited knee movement.
Shoulder joint pain
Shoulder joint pain is often associated with sprains, tendonitis or trauma. Various joint diseases, such as rotator cuff tears, can also cause shoulder pain.
The shoulder is one of the most mobile and flexible joints in the body. This makes it vulnerable, which is why about a third of people experience shoulder pain at least once in their lives.
Elbow joint pain
Pain in the elbow joint is often caused by strain on the joint, injury or inflammation. Pain is most often caused by moving the elbow. At the same time, swelling or numbness in the arm may be noticeable. Elbow pain is also often associated with activities that involve repetitive movements, such as tennis.
Hand joint pain
Pain in the wrist joint can be caused by injury, inflammation or nerve entrapment. Pain can be localised in the hand or spread to the arm. It is often associated with joint problems such as carpal tunnel syndrome or arthritis. Pain may be accompanied by numbness and weakness in the hands.
Hip joint pain
Hip pain is less common than knee or shoulder pain and can be more difficult to diagnose. Pain can be localised in the groin or lower back, or can spread to the hips, so determining the true cause can sometimes be challenging. However, hip pain is most often associated with tendon, ligament and muscle injuries or arthritis.
Nocturnal joint pain
There are several reasons why people may experience more intense joint pain at night or early in the morning.
Osteoarthritis, which is characterised by wear and tear on the cartilage and inflammation of the joints, can cause more pain at night. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the joints, can also contribute to night-time joint pain.
Migrating joint pain
Migratory joint pain, on the other hand, can be associated with nervous disorders such as nerve entrapment.
Joint problems can also contribute to migratory joint pain. Then, the pain may occur in several different joints, migrating from one to another.
It is important to pay attention to the symptoms of joint pain and, if you feel them, consult a specialist in good time to help identify the real cause of the pain and prescribe the right treatment. Only with the right treatment and healthy lifestyle choices can joint pain be controlled and quality of life improved.
Causes of joint pain
Joint pain can be caused by a variety of factors affecting the joints and surrounding tissues. The most common causes of joint pain are:
Joint inflammation. Often, joint pain can be caused by inflammation, such as arthritis. Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of the joints where the body’s immune system attacks the joints, causing pain and swelling. The most common types of arthritis are rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Trauma and injury. These are also common causes of joint pain. Injuries to ligaments, tendons or cartilage can cause pain and joint dysfunction.
Heavy loads. Excessive load on a joint can also cause joint pain. Heavy exercise, constant strain or even obesity can increase the stress on the joints and damage their health.
Age. Age is also an important factor in joint pain. As we age, cartilage loses elasticity and the amount of fluid in the joints decreases, increasing the risk of joint pain.
Genetic factors. Genetic factors can also affect joint conditions. Some people may have an inherited predisposition to certain joint diseases that increase the likelihood of joint pain.
Diseases. Certain diseases can cause joint pain that a person did not have before.
For prevention and treatment, it is important to identify the cause of joint pain and consult a health professional who will determine an appropriate treatment plan. Regular exercise, a healthy diet and an appropriate body weight can help maintain joint health.
Treatments for joint pain
Joint pain treatment is a complex procedure that uses a variety of techniques to relieve pain, restore mobility and improve joint health. The main treatments for joint pain include:
Drug therapy. Pain killers are often used to treat joint pain. Non-steroidal drugs reduce inflammation and pain. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis are often prescribed immunosuppressants or other drugs to regulate the immune system. Medication treatment can take different forms – topical medications, tablets or infusions, depending on the condition. Intravenous drugs affect the whole body, not only fighting pain but also acting on the site of inflammation and stopping the development of additional inflammatory processes.
Physiotherapy. This is an important component of joint treatment, especially after trauma or injury. Physiotherapy includes a range of exercises, massage and other physical methods to strengthen muscles, improve joint mobility and reduce pain. A physiotherapist can prescribe an individual treatment plan based on the patient’s needs and the cause of the joint pain.
Therapeutic exercise. These are specially designed exercises to strengthen specific joints and muscles. They are designed to relieve pain and restore joint mobility. This is an important aspect of treatment to maintain joint health. Exercise can also be an excellent way to prevent joint pain.
Intravenous therapy. This can be a useful way to improve joint health during sports and to not only relieve joint pain, but also to ensure that the body is fully supplied with the vitamins it needs.
Intense sports often increase the load on the joints, which can cause pain and other discomforts. Intravenous therapy can be useful to provide the body with rapid and efficient absorption of vitamins, minerals and antioxidants.
“Drops Clinic offers a range of IV therapy courses, such as ‘Back Pain Relief’ and ‘Vitamin Cocktail’, which are designed to support the health of sports people.
Surgical intervention. When conventional methods don’t work or the damage to the joint is particularly severe, surgical intervention may be necessary. A surgeon may perform arthroscopy, replace the cartilage or even perform a joint replacement.
Home treatment. This is the first step in dealing with joint pain. Uncomplicated injuries, sprains or inflammation can be treated at home. Rest, cold compresses and bandages can help. However, if the pain persists for a few days, it is worth consulting a specialist. This is a signal that professional help is needed.
It is important to note that the best treatment plan depends on the specific joint problem, its complexity and the individual needs of the patient. Therefore, a consultation with a health professional is essential in order to develop a suitable treatment plan for joint pain.
How do I care for my joints after treatment?
After treatment, it’s important to take regular care of your joints to maintain their health and prevent recurrence. Exercises and therapies prescribed by your doctor are an important part of joint care, helping to strengthen muscles, improve joint mobility and prevent new problems. Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming or yoga exercises, can be useful to keep joints flexible.
A healthy diet is also an important part of maintaining joint health. It is also important to monitor your body weight to avoid putting extra strain on your joints.
Regular visits to a specialist should be kept in mind. A comprehensive and regular joint care plan will help you to maintain mobility and reduce the chance of recurrence of pain or other joint problems in the future.
If you experience joint pain, contact the Drops Clinic specialists. Our expert team of doctors is always ready to help you regain your quality of life. Our team is made up of professionals with the highest qualifications and skills, using only the latest state-of-the-art medical equipment. After listening to your complaints and preferences, and based on the detailed tests carried out, our professional doctors will select the most suitable treatment for you.
Frequently asked questions:
When do I need to see a doctor if my joints hurt?
You should see a specialist if you notice persistent or increasing joint pain, swelling, mobility restrictions or other unusual symptoms. If the pain is recurrent, lasts for a long time or causes severe discomfort, it is important to consult a doctor, as these symptoms may signal more serious problems. In this case, it is important not to delay seeing a specialist and to seek professional treatment immediately.
What should be avoided in case of joint pain?
If you have joint pain, it’s important to avoid factors that can aggravate the condition. In particular, avoid overloading the joints and additional trauma. Avoid prolonged sitting or standing, which can put strain on the joints. Try to rest as much as possible to allow the joints to recover.