Blood is a vital component of our body that provides oxygen to all cells. When we breathe in fresh air, red blood cells cling to oxygen molecules, which then travel through the bloodstream, reaching every corner of the body. This amazing biological mechanism not only supports cell renewal, but also energises the body, strengthens the immune system and provides other essential vital functions.
Oxygen is the basic element necessary for the existence of all living organisms. Homeostasis requires a balance between the entry of oxygen into the body and its consumption. In the human body, the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are the most important systems responsible for bringing oxygen into the body and maintaining the stability of the internal environment, and in this article, we will explore the problems associated with oxygen deficiency and present various ways to naturally and medically raise oxygen levels in the body.
What is hypoxia?
Hypoxia is a medical condition that is characterised by a lack of oxygen in our body tissues. This problem can arise from a variety of causes, such as insufficient oxygen in the environment, problems in the respiratory or circulatory systems, or even the inability of cells to use oxygen properly. Depending on the cause and localisation, hypoxia can have different health consequences and can promote the onset of various symptoms.
Are hypoxia and hypoxaemia the same thing?
The terms hypoxaemia and hypoxia are not synonymous. Hypoxaemia is a decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood. Hypoxia is the insufficient oxygen in the tissues. The two conditions do not always occur together. Hypoxaemia can occur without hypoxia, e.g. an increase in haemoglobin to compensate for the lack of oxygen. Hypoxia is also possible in the absence of hypoxaemia (e.g. hypoperfusion). The main difference between these terms is that hypoxia is a lack of oxygen in the tissues, whereas hypoxaemia is a lack of oxygen in the blood.
Both diseases can cause similar symptoms, such as shortness of breath, confusion or increased heart rate, but not all symptoms of hypoxia are characteristic of hypoxaemia, and vice versa.
This means that treatment strategies and diagnostic methods are specific to each condition and require care. Understanding the differences between these conditions is vital for the correct diagnosis and effective treatment of patients who suffer from oxygen uptake problems.
| General symptoms | Characteristic of hypoxia only | Characteristic of hypoxaemia only |
| Skin colour changes (blue to cherry red). | Anxiety. | Severe headaches. |
| Confusion. | Headaches. | Seizures. |
| Cough | Increased blood pressure. | |
| Abnormal heart rhythm. | Difficulty breathing. | |
| Impaired breathing. | Tachycardia. | |
| Shortness of breath. | Hypotension | |
| Sweating. | Irregular heart activity. | |
| Wheezing in the airways. | Coma (in extreme cases). |
Hypoxia refers to a condition in which the tissues in the body are deprived of oxygen. This can be due to a variety of causes, including reduced oxygen levels in the ambient air, impaired respiratory or circulatory systems, or the inability of cells to utilise oxygen due to biochemical disorders. Hypoxia can affect individual organs or the whole body, which is why the disease is classified into several types.
The different types of hypoxia differ in the system in which the disorder occurs:
- Exogenous hypoxia: This is a condition where there is a lack of oxygen in the environment, such as in high mountains or confined spaces.
- Respiratory hypoxia: Occurs when the respiratory organs are unable to supply oxygen to the blood effectively, due to respiratory disorders such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Circulatory hypoxia: Occurs when organs and tissues are inadequately supplied with blood due to a circulatory disorder (haemorrhage, cardiovascular disorders)
- Blood (haemic) hypoxia: This condition occurs when haemoglobin in the blood is unable to transport oxygen efficiently, due to problems such as anaemia or poisoning such as carbon monoxide.
- Tissue (histotoxic) hypoxia: Occurs when tissues are unable to make good use of the oxygen that reaches them, for example due to certain toxins that interfere with cellular activity..
What is the normal level of oxygen in the blood?
Blood oxygen levels are an important indicator of health, reflecting how much oxygen is bound in red blood cells. This level can be determined by blood tests or by using a pulse oximeter, an oxygen machine that measures the percentage of oxygen saturation (SpO2), which is the basic unit of measurement of blood oxygenation.
The optimal SpO2 level is between 95 and 100 percent. People with lung disease may have a slightly lower SpO2 level, usually between 88 and 92 per cent. If the SpO2 falls below 95 per cent, it can signal possible hypoxaemia, which in turn can cause tissue hypoxia. This condition is extremely serious and cannot be ignored, especially in the presence of pre-existing medical conditions, as it can lead to serious complications.
How to raise blood oxygen levels?
Žmogaus gyvybingumui didelę įtaką daro deguonies kiekis kraujyje. Pakankamas deguonies kiekis kraujyje ne tik gerina bendrą savijautą, bet ir stiprina imuninę sistemą, gerina miego kokybę ir energijos lygį. Norint padidinti deguonies kiekį kraujyje, galima taikyti įvairius metodus – nuo sveikesnio gyvenimo būdo pasirinkimo iki specialių kvėpavimo pratimų ir klinikinės terapijos.
Natural ways
- Indoor ventilation – ventilate your rooms regularly by opening windows and walking in the fresh air to encourage greater oxygen uptake.
- Giving up bad habits – by giving up smoking, a significant improvement in blood circulation and oxygen levels can be seen within two weeks.
- Growing houseplants – grow houseplants that purify the air by removing carbon dioxide and enriching it with oxygen, thereby increasing the oxygen level in the room.
- Breathing exercises – practise simple exercises such as deep, slow breathing to increase oxygen uptake.
- Use a pulse oximeter – use an oxygen machine at home to check blood oxygen levels and monitor improvements.
Baro camera
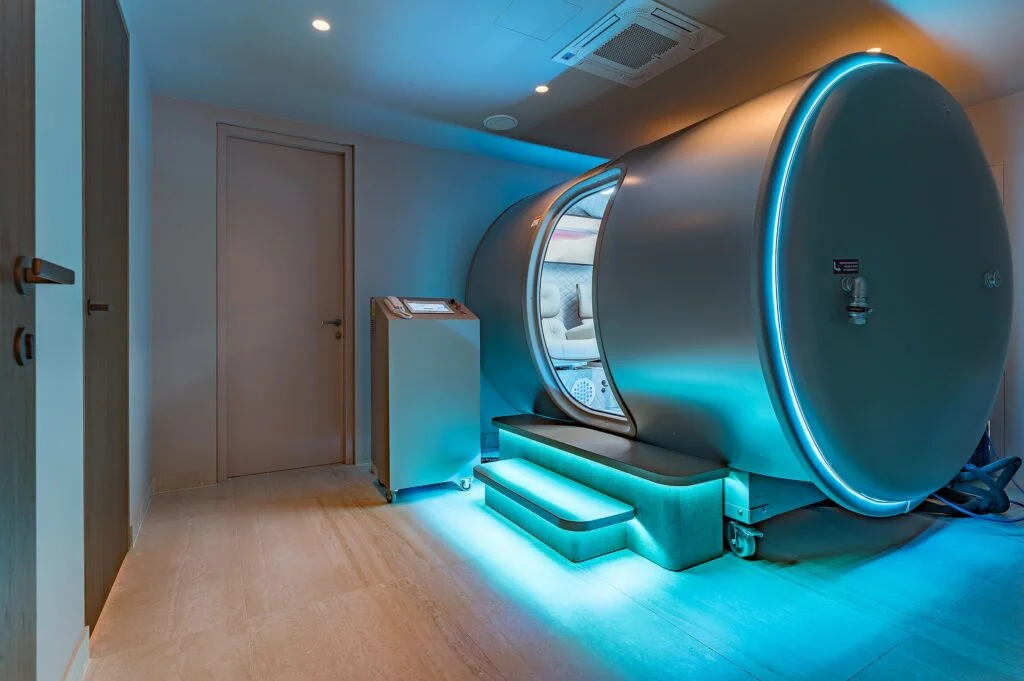
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBO) is a revolutionary treatment method where patients breathe 94% pure oxygen in a special bar chamber. This advanced therapy allows the body to absorb up to 5 times more oxygen molecules than normal, thus improving overall health, delaying the ageing process, promoting faster wound healing and effectively reducing inflammation and infections. Thanks to the maximum oxygen saturation, the blood transports oxygen more efficiently to the body, which is particularly important for the recovery of tissues after injuries or surgery, activates metabolism, improves blood circulation and promotes the detoxification and regeneration processes, helping the body to get rid of harmful substances and rebuild damaged cells.
Ozone therapy
Ozone therapy is a safe and effective way to increase the amount of oxygen in your blood. This treatment uses a mixture of ozone and oxygen, which is produced in a special generator from medical oxygen. During the treatment, the patient’s blood is drawn and saturated with ozone gas and then returned to the body. This method improves blood circulation, strengthens the immune system and improves nerve function, thanks to the anti-inflammatory effect of ozone. Ozone therapy is highly effective, does not cause allergies or side effects, and positive results are visible after the first treatment or course of treatments.
To summarise
Maintaining adequate oxygen levels in the blood can effectively prevent hypoxia and hypoxaemia, which can cause serious health problems. Ventilation, healthy habits such as smoking cessation and staying in well-ventilated rooms are important for optimal oxygen levels. In addition, medical solutions such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy and ozone therapy can provide significant relief, especially for more serious health conditions. A combination of different methods is the most effective way to ensure that the body always has enough oxygen.