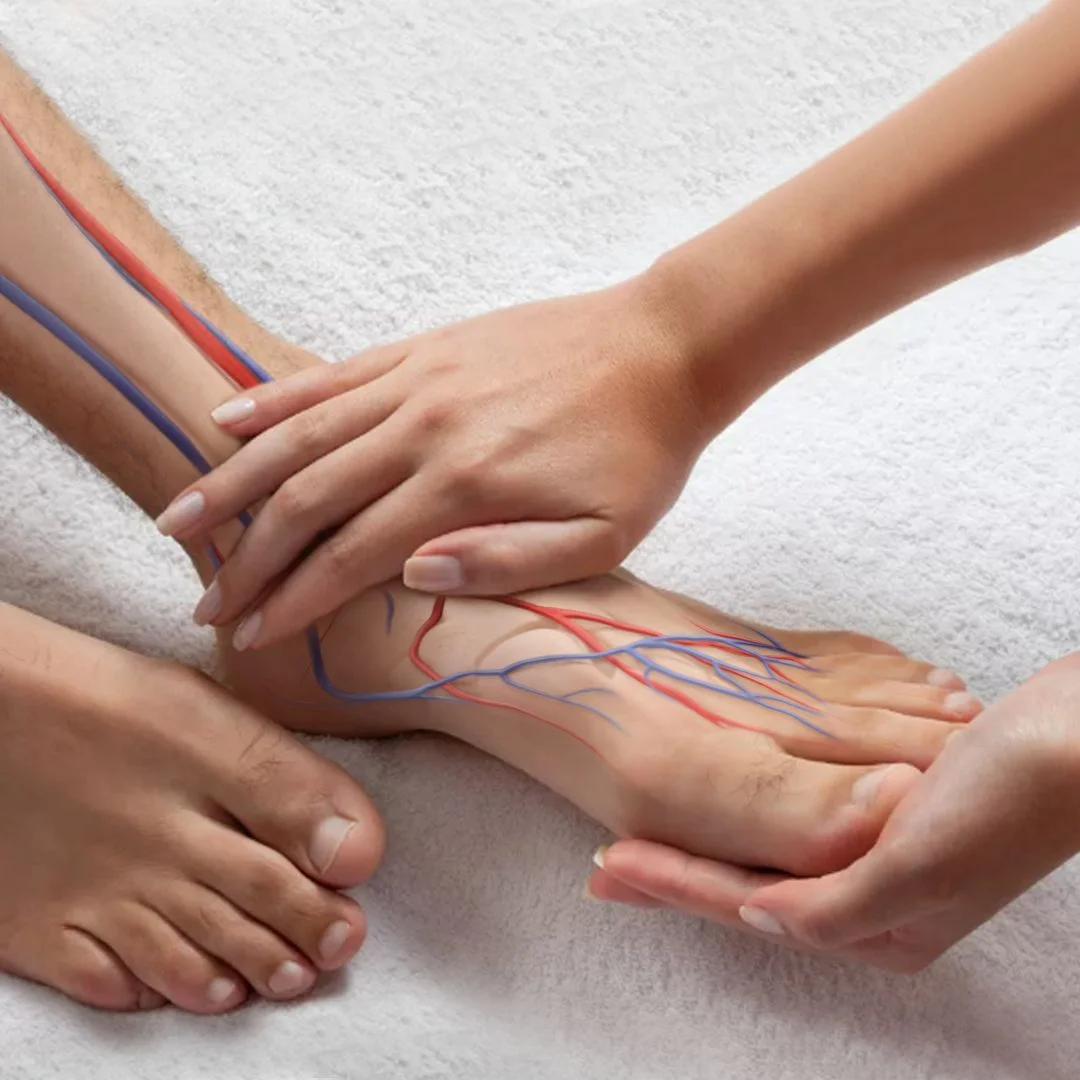
The circulatory system – the organ system made up of our heart, blood vessels and blood – is one of our body’s most important systems, and its smooth functioning is essential to keep the body running. This system is responsible for the most important functions of our body – carrying oxygen, nutrients, electrolytes and hormones to our cells and removing unnecessary substances such as carbon dioxide. Various disorders of this harmonious system are quite common, but despite this, many people do not immediately recognise circulatory disorders. For this reason, it is extremely important to know how to recognise a circulatory disorder, which means being aware of the different types of circulatory disorders, their symptoms, prevention and treatment.
Types of bleeding disorders
Circulatory disorders can lead to various cardiovascular diseases, depending on where in the circulatory system they occur. The list of these disorders is very broad, so let’s take a look at the main ones:
Arterial hypertension
Arterial hypertension – a long-term increase in arterial blood pressure when the force or pressure of blood flowing through the blood vessels is too high, detected by repeated measurements. Doctors consider blood pressure of 140/90 mmHg and above to be high blood pressure. This is a very dangerous condition in the long term, as it can lead to various health problems such as heart disease, stroke and visual impairment.
Varicose veins in the legs.
Varicose veins are swollen and enlarged veins that are usually superficial, i.e. close to the surface of the skin. Varicose veins are most often found in the veins of the legs, due to increased pressure when standing and walking. Varicose veins are usually bluish, purple or red in colour. They are also characterised by swelling and bulging. If left untreated, varicose veins can lead to very serious complications. One of them is trophic ulcers. An ulcer is an open gateway for infection to enter the body.
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
This is a condition in which blood cannot flow freely to the heart muscle due to narrowing or blockage of blood vessels. This is usually caused by a build-up of fatty deposits (such as cholesterol) inside the arteries. If left untreated, this disorder can lead to heart rhythm disturbances, myocardial infarction or heart failure.
Thrombosis
This is a very serious and severe condition where one or more blood clots form in the blood vessels or heart. When a clot forms, blood flow is blocked at the site. If the clot breaks off, it can become stuck, at a site critical for vital functions. This can lead to life-threatening conditions such as stroke, heart attack, pulmonary embolism with shortness of breath.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease of the artery wall, a process of stiffening and narrowing of the arteries that starts unnoticed and develops silently. During this process, atherosclerotic plaques (atheromas) form in the arteries. Atherosclerosis damages the vital blood vessels – the arteries – through which blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues. Atherosclerotic plaques are most commonly found in the heart, popliteal, carotid, iliac arteries and aorta.
Heart attack
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is severely reduced or completely blocked, preventing the muscle from getting enough oxygen. Vascular blockages are most often caused by fatty deposits in the coronary arteries. A heart attack can be fatal or have extremely serious consequences, which is why it is essential to seek immediate help.
Stroke
A stroke is a serious, life-threatening medical condition in which blood flow to the brain is disrupted due to a blocked or ruptured blood vessel. A stroke carries a high risk of paralysis and death, so it is important to seek medical help as soon as possible. The sooner help is given, the less chance of harm. The main symptoms that help you recognise a stroke are:
- Sudden weakness on one side of the body
- Speech and orientation are impaired.
- Vision in one eye is impaired.
- Balance problems, dizziness.
- Severe headache (due to ruptured blood vessel).
Symptoms of a bleeding disorder
Circulatory disorders must be recognised and treated in time. These disorders can present with a wide range of symptoms, which allow early treatment and avoid serious health complications. Some of these symptoms have been mentioned in the discussion of the different types of disorders, and the following are the main common signs that indicate possible circulatory disorders:
- Leg swelling
Impaired blood circulation in the legs can cause oedema, which can manifest as swelling in the legs or feet. Edema, also known as fluid retention, is caused by excess fluid in the tissues. This is caused by increased pressure in the blood vessels.
- Cold extremities
Poor circulation makes the hands and feet feel much colder than the rest of the body. When blood cannot flow at its normal rate, a person can experience temperature fluctuations in the skin and nerve endings in the arms and legs.
- Numbness and tingling in the extremities
Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet are some of the main signs of poor circulation, which occur when blood does not reach the extremities properly.
- Headache. Feelings of numbness and dizziness.
Headaches, accompanied by feelings of numbness and dizziness, can be caused by a variety of reasons, including fluctuations in blood pressure or constricted blood vessels in the neck that affect blood flow to the brain.
- Difficulty with memory and attention, more frequent and faster fatigue.
Memory impairment is one of the symptoms of insufficient blood circulation. If the brain doesn’t get enough blood, memory, hearing and co-ordination can be affected. These also make people tired more quickly.
- Digestive disorders
Poor blood circulation is one of the signs of gastrointestinal problems. Reduced blood flow can lead to: abdominal pain, diarrhoea, bloody stools and constipation.
What are the consequences of circulatory problems?
Circulatory disorders are associated with many negative consequences. These disorders can cause a variety of everyday discomforts, such as persistent pain, numbness, tingling or a feeling of coldness in areas of the body where blood flow is compromised. In addition, dizziness, incoordination and muscle weakness can make everyday life very difficult. Circulatory problems also pose a high risk of serious health problems and life-threatening conditions. Serious circulatory problems increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
How to treat circulatory disorders?
Treatment of bleeding disorders depends on the cause and the severity of symptoms. It is important to react promptly to the signs sent by the body and to know what to do in the event of a circulatory disorder. Here are some common treatments and recommendations:
Medicines to improve blood circulation
With regard to the medical treatment of circulatory disorders, we can see that there is a wide range of different medications. Let’s discuss some of the main ones:
- ACE inhibitors – prescribed for high blood pressure or heart failure.
- Anticoagulants – help prevent blood clots.
- Statins – to help lower plasma cholesterol.
- Diuretics – help to remove extra fluid from the body and treat high blood pressure and heart failure.
- Beta-blockers – used to treat various heart conditions.
- Calcium channel blockers – treat high blood pressure, various arrhythmias.
- Vasodilators – these are vasodilators. Your doctor may prescribe vasodilators to treat high blood pressure, chest pain or heart failure.
Certain circulatory disorders also require surgical interventions, such as cardiac surgery, percutaneous coronary intervention and minimally invasive heart surgery.
Healthy lifestyles and prevention
Of course, as with many health problems, we can expect a better outcome if we take preventive measures before serious health problems arise. Different circulatory disorders require specific care, but there are some general recommendations. One of the most important factors in preventing circulatory diseases is regular health check-ups. Many people have risk factors they are not even aware of. A doctor can spot problems early, before they become more serious.
Another crucial aspect is changes in diet and lifestyle. A good diet and lifestyle can both help prevent circulatory diseases and improve health after they have occurred. It is therefore important to:
- Follow a heart-healthy diet – include foods in your diet to improve blood flow. Foods such as chilli peppers, pomegranates, beetroot and berries have properties that help to fight vascular disease effectively.
- Incorporate aerobic exercise or other forms of physical activity into your daily routine – do sports activities and exercises to improve blood flow, such as squats, walking, cycling and yoga.
- Avoid stress as much as possible and learn and apply stress reduction techniques.
- Avoid smoking, alcohol and other psychoactive substances.
Dietary supplements to improve blood circulation
If you want to improve blood circulation with dietary supplements, it’s worth paying attention to:
coenzyme Q10. Coenzyme Q10 is particularly important for the heart’s function, as it needs to produce large amounts of energy to keep beating. Numerous scientific studies have shown that people with heart disease who take coenzyme Q10 have dramatic improvements in their condition: they have less chest pain, they don’t feel tired, their heart beats stronger and they have much more physical strength.
- L-Arginine – among other important roles in the body, this amino acid can act as a vasodilator, which can open up arteries and improve blood flow.
- Iron – an essential mineral for our body, it is needed to form haemoglobin, which serves the function of carrying oxygen in the blood. Iron is an essential part of healthy blood circulation. Although this mineral is found in a wide range of foods, our bodies do not always absorb enough of it, so we can use iron supplements after consulting our doctor.
- Omega-3 – There are many studies linking omega-3 fatty acids to better cardiovascular health. Omega-3 fatty acids can improve blood circulation by reducing triglyceride levels. Omega-3s are also thought to reduce the risk of blockages in the arteries by helping to prevent platelet build-up.
Complementary therapies to improve blood flow
Ozone therapy can also help improve blood circulation. In this procedure, a small amount of blood is taken from the patient so that it can be saturated with ozone gas and then slowly injected into a vein. Ozone therapy can help to improve blood flow, reduce inflammation and blood thickness, and dilate blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more easily.
Another equally effective treatment is NAD+ (Anti-Aging) therapy. Studies show that NAD+, a compound found in every cell in our body, plays an important role in maintaining cardiovascular health. NAD+ helps regulate the heart’s energy production and metabolism, and its depletion can contribute to heart problems as we age. This treatment can contribute to improving blood circulation, reducing inflammation and lowering blood cholesterol.
Apibendrinimui
Kadangi kraujotakos sutrikimai gali sukelti rimtas sveikatos problemas, yra būtina juos laiku atpažinti ir tinkamai gydyti. Ankstyva diagnostika ir individualus gydymo planas, įskaitant vaistus, sveiką gyvenseną bei sveikatai naudingus papildus bei terapijas, yra esminiai veiksniai, padedantys išvengti ligos progresavimo ir ilgalaikių pasekmių sveikatai. Visada svarbu konsultuotis su gydytoju ir aptarti asmeninius sveikatos poreikius, siekiant užtikrinti efektyviausią gydymo eigą.